Versatile Shredding Services for Your Unique Security Needs
Discover our array of paper shredding solutions designed to accommodate the specific security requirements of various operations. Locally based and accredited, ZircoDATA Singapore is your trusted shredding services partner.

One Time Shredding

Regular Scheduled Shredding

Mobile On-site Shredding

Specialty Shredding

Hard Drive Destruction

Media Destruction
Protecting your confidential information is our mission
Leading organisations choose ZircoDATA to provide document security, ensure information privacy and consistently achieve compliance.
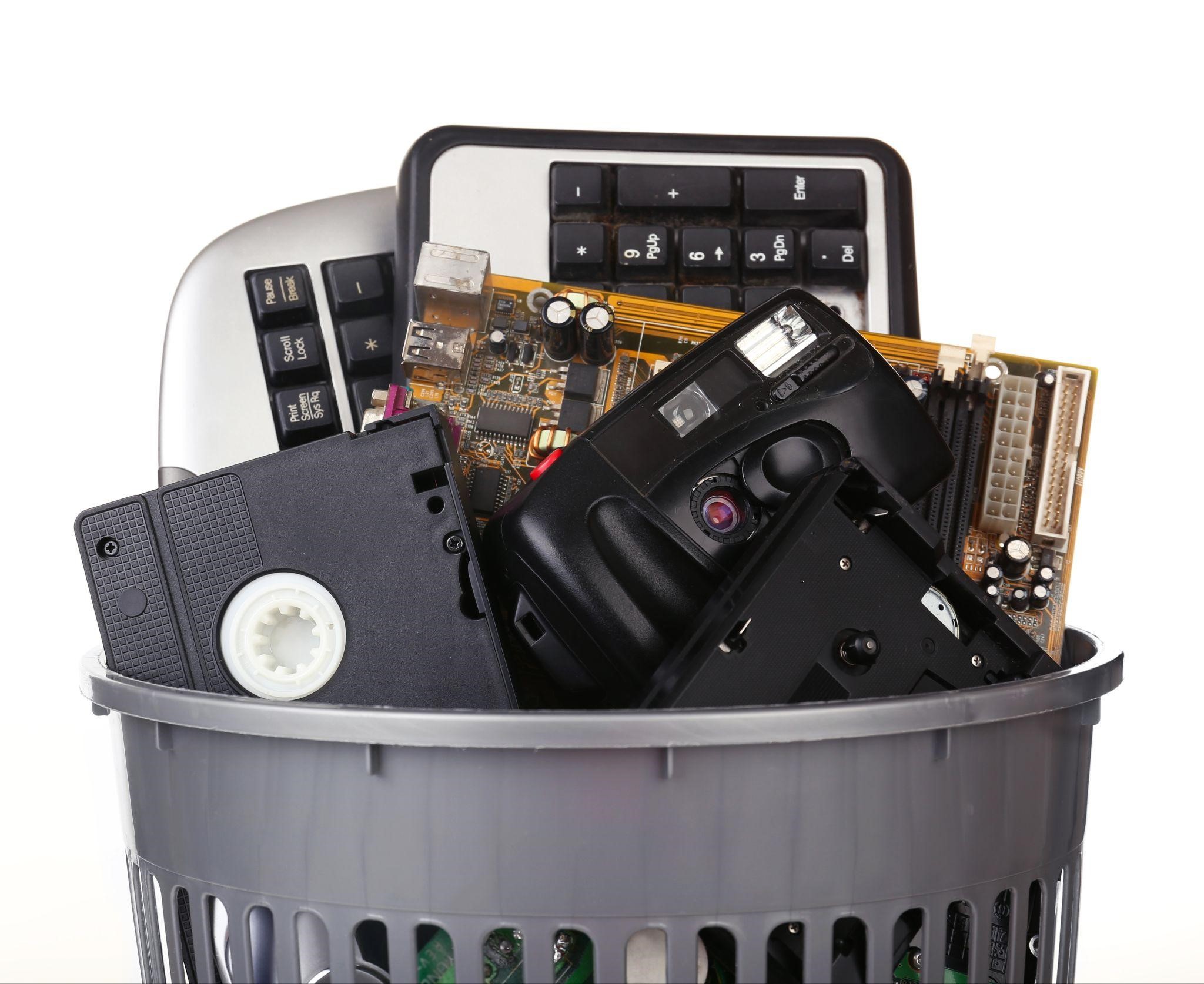
We securely destroy non-paper sources of confidential information.
Hard Drives

Media

Medical Records

X-Rays
Credit Cards

ID Badges

Branded Goods

Promotional Items

How it works

1
Get Free Quote
Get a customised quote for the paper shredding service you need.

2
Select Date of Service*
Choose when and where you want your service.
*Subject to shred centre availability

3
ZircoDATA Arrives
We arrive on the scheduled date, collect your confidential information and securely shred it.

4
Records Destroyed
All services come with a Certificate of Destruction for your records. All destroyed paper is securely recycled.
The Strategic Edge To Hiring Paper Shredding Services
Employing professional document shredding services from ZircoDATA is a decisive step towards fortifying your operations and safeguarding your organisation's reputation. Here are more reasons why it's a prudent measure for most companies:
-
Regulatory Compliance Made Easy
Enlisting professional paper shredding services helps your organisation adhere to industry-specific legal and regulatory requirements. By systematically eliminating outdated or unnecessary documents, you ensure only relevant records are retained, promoting operational transparency and accountability.
-
Robust Defence Against Data Breaches
Data breaches can have catastrophic effects on a company’s brand image and financial standing. Employing meticulous document shredding and destruction practices substantially diminishes the risk of sensitive information falling into the wrong hands, thus providing a solid foundation for your data security strategy.
-
Cost Efficiency and Space Optimisation
Outsourcing shredding services translates to significant cost savings, eliminating the need for in-house shredding equipment, maintenance and personnel. Moreover, regular paper shredding liberates valuable office space previously occupied by obsolete documents. This streamlined approach boosts operational efficiency while reducing unnecessary expenditures.
-
Environmental Responsibility
Engaging with a paper shredding service that recycles the shredded material demonstrates your organisation’s commitment to environmental sustainability. By opting for eco-conscious document destruction, companies not only adhere to a high standard of data security but also contribute positively to environmental conservation efforts.
-
Certified Destruction for the Added Layer of Confidence
When you entrust document destruction and paper shredding needs to ZircoDATA, you receive a certificate of destruction for every service. This document serves as verifiable proof that all sensitive materials have been securely destroyed, aligning with legal and industry standards. It’s an indispensable asset for audit trails, providing tangible evidence of compliant data handling practices. This certification augments the trust and confidence of stakeholders and fortifies the integrity of your data protocols.
-
Employ Superior Shredding Solutions Now
Unlock a higher level of data security with ZircoDATA’s tailored shredding services, extending from paper to media destruction, hard drive and speciality shredding. Contact us for a quote or further details, and take a decisive step towards safeguarding your organisational integrity. Leverage our expertise and elevate your organisation’s security and compliance today.
You Can Trust us to Protect Your Information
Leading organisations choose ZircoDATA to provide document security, ensure information privacy, and enable compliance.




